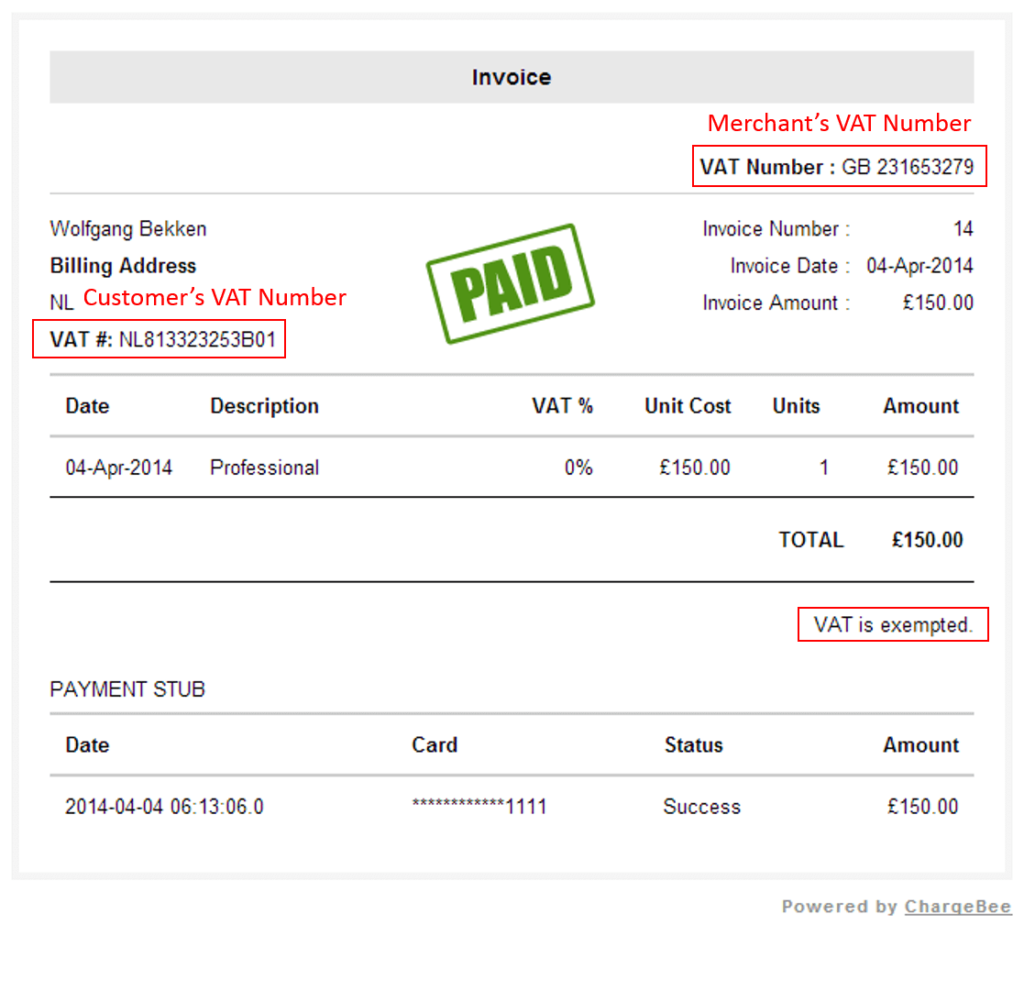
Every business with VAT registration provides a unique registration number on its invoice. An individual running a business can ask their VAT-registered supplier to provide a VAT number to reclaim the VAT paid.
Credit: Wis
Find VAT Number
The end level consumers of the supply chain are liable to VAT payments. Almost every goods and service in the UK has VAT on it.
But, a business can add VAT to its supplies only when they register for VAT. That means it becomes necessary to provide a business’s VAT number when charging VAT.
The contents of the blog post are:
Table of Content
What is Value Added Tax or VAT?
VAT is an acronym for Value Added Tax. It is the consumer tax applicable to purchasing goods and services. A seller collects the tax on behalf of consumers and pays to the HMRC.

The standard VAT rate in the UK is 20%. Some supplies are can claim for VAT exemption, like statutory fees, commercial land and buildings, education, financial services, and health services.
The table below shows three VAT rates in the UK, depending on the type of products and services.
| VAT rate | Applicable on | |
| Standard rate | 20% | On most goods and services |
| Reduced rate | 5% | Some goods and services like children’s car seats, energy-saving materials, electricity, gas, maternity pads. |
| Exempt | Exempt | There are some essential goods and services that are exempt from VAT, for example: education, insurance, health care service. |
| Zero rate | 0% | Zero-rated goods and services like newspapers, cooking oil, equipment for disabled people, fruits and vegetables, salt, water. |
Check our blog post: A Complete Guide to VAT Codes: the Full List
A business can charge VAT to consumers only when registered for VAT. They will have a unique registration number from the HM Revenue and Customs.
Businesses earning a profit above the primary threshold level must register for VAT. The primary threshold level for 2021-22 is £85,000 in the UK. If your turnover falls below that level in the next year, you can apply for de-registration.
What is a VAT registration number?
It is a unique number of any VAT-registered business. Owners can find this number on their registration certificate from the HMRC.
The VAT number is a set of characters. The first two letters are the country code of the registered business, and the remaining 2-13 are alphanumeric characters of the VAT registration number.
Where can I find Vat Number?
A business can register for VAT anytime it makes a turnover above the primary threshold level for VAT in the UK and can deregister otherwise. HMRC provides a certificate that mentions the unique VAT registration number on successful registration.
An individual can find VAT number from the invoice, national tax office page, official accreditation, and VIES.
In this table, we can see the different country codes under the European Union.
| Country Name | Country code | Characters |
| Austria | AT | 9 Characters starting with U |
| Belgium | BE | 10 Characters |
| Bulgaria | BG | 9 or 10 Characters |
| Cyprus | CY | 9 Characters ending with a letter |
| Czech Republic | CZ | 8, 9, or 10 Characters |
| Denmark | DK | 8 Characters |
| Estonia | EE | 9 Characters |
| Finland | FI | 8 Characters |
| France | FR | 11 Characters |
| Germany | DE | 9 Characters |
| Greece | EL | 9 Characters |
| Hungary | HU | 8 Characters |
| Ireland | IE | 8 Characters |
| Italy | IT | 11 Characters |
| Lithuania | LT | 9 or 12 Characters |
| Luxembourg | LU | 8 Characters |
| Latvia | LV | 11 Characters |
| Slovakia | SK | 10 Characters |
| Malta | MT | 8 Characters |
| The Netherlands | NL | 12 Characters and the 10th Character is B |
| Poland | PL | 10 Characters |
| Portugal | PT | 9 Characters |
| Romania | RO | Between 2 – 12 Characters |
| Sweden | SE | 12 Characters |
| Slovenia | SI | 8 Characters |
| Spain | ES | 9 Characters |
| United Kingdom | GB | 9 Characters |
Checking a VAT number is valid
A VAT registration number is not a random number, and an individual can check its validity. To verify a VAT number, let us follow these steps:
- Take a VAT number. For example, GB 211546303.
- Place the digits vertically, excluding the first two letters (country code) and the last two numbers.
- Multiply the remaining numbers with 8 to 2 (descending order).
2×8=16
1×7=7
1×6=6
5×5=25
4×4=16
6×3=18
3×2=6
● Add all these numbers.
16+7+6+25+16+18+6 = 94
● Subtract the above value with 97 until it becomes a negative number.
94-97 =-03.
● This negative number matches with the last two digits of the VAT number, and the VAT number is valid.
Here is another example of how to check a VAT number’s validity:

Whenever you start a new business or work with a new supplier, it is essential to check the VAT registration number. Customers may ask you for a valid VAT number as you can ask for it from your supplier.
Ways to check whether a VAT number is valid or not
To check the validity of the VAT registration number, you can follow two steps:
● Use VAT Checker: The easiest way will be to use our online VAT Checker to check whether a VAT number is valid or not. You can check both UK – GB Vat and European EU vat.
○ Visit the official European Commission VIES website
○ Enter the VAT number of the business, including the country code
○ If the registration number is valid, it will confirm its validity and share the name of the business and its registered office address.
● Contact HMRC: Any individual can call the VAT helpline number of HMRC on weekdays between 8 am and 6 pm to check the validity of the VAT registration number.
What if the VAT number is not valid?
If the number is not valid, you need to ask the owner or the supplier to provide the correct number. Even after reviewing that number, it remains invalid; you must inform them immediately. Owners can further contact the HMRC to verify their registration number.
It is essential to have a valid VAT number as you cannot charge VAT on goods on services you sell. Additionally, if you reclaim VAT, HMRC will ask you to provide the correct VAT number of the supplier or reject your claim.

Wrapping up
You can check whether a given VAT number is valid or not using the methods mentioned earlier. Many fraudulent activities occur with a fake VAT number. You may be charged wrongly for VAT even when the company didn’t register itself for VAT. Therefore, it is necessary to check the VAT number before paying them.
Errors in the VAT number may occur due to minor mistakes. You can consult with the HMRC and correct it immediately.










Leave a Reply